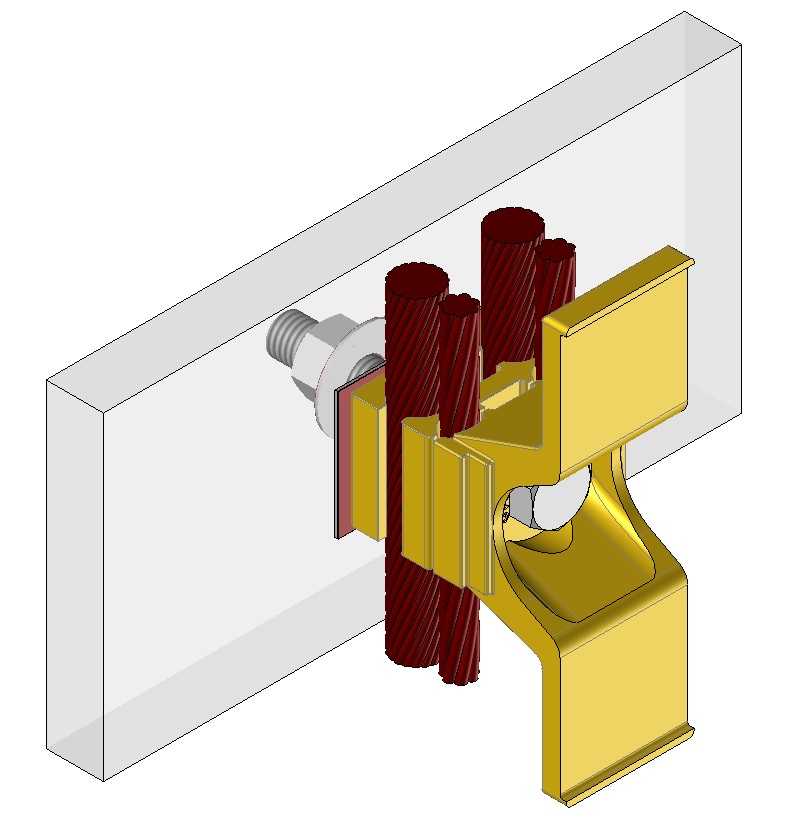
Physical Phenomena
Discover the physics behind the galvanic corrosion
Description of the galvanic corrosion phenomenon
Galvanic corrosion is the result of the following three conditions:
- Metals of different nature
- Contact between these metals
- Presence of water, thus oxygen
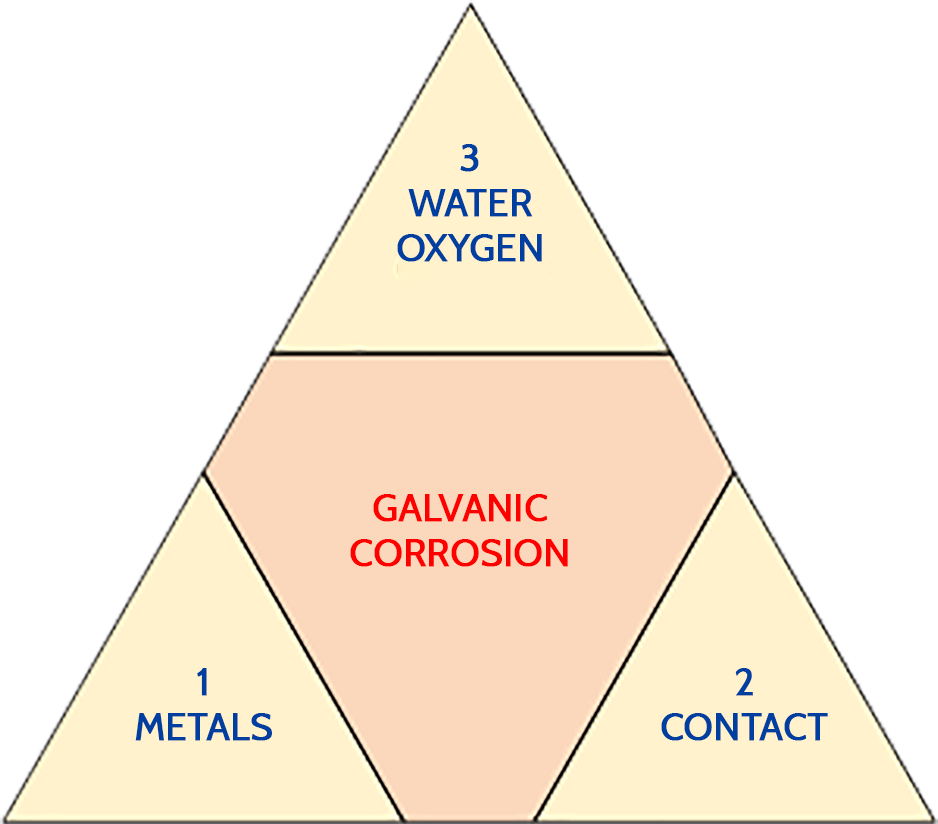
To reduce galvanic corrosion it is therefore necessary eliminate one of the three conditions. The suppression of metals and water or oxygen present being impossible, it is recommended to avoid the direct contact between metals of different nature.
Galvanic corrosion induces an electrical current flowing between metals. This current generates a metalic ion exchange. The anode releases metalic ions, conversely, the cathode is charged with ions:
%20(1).png)
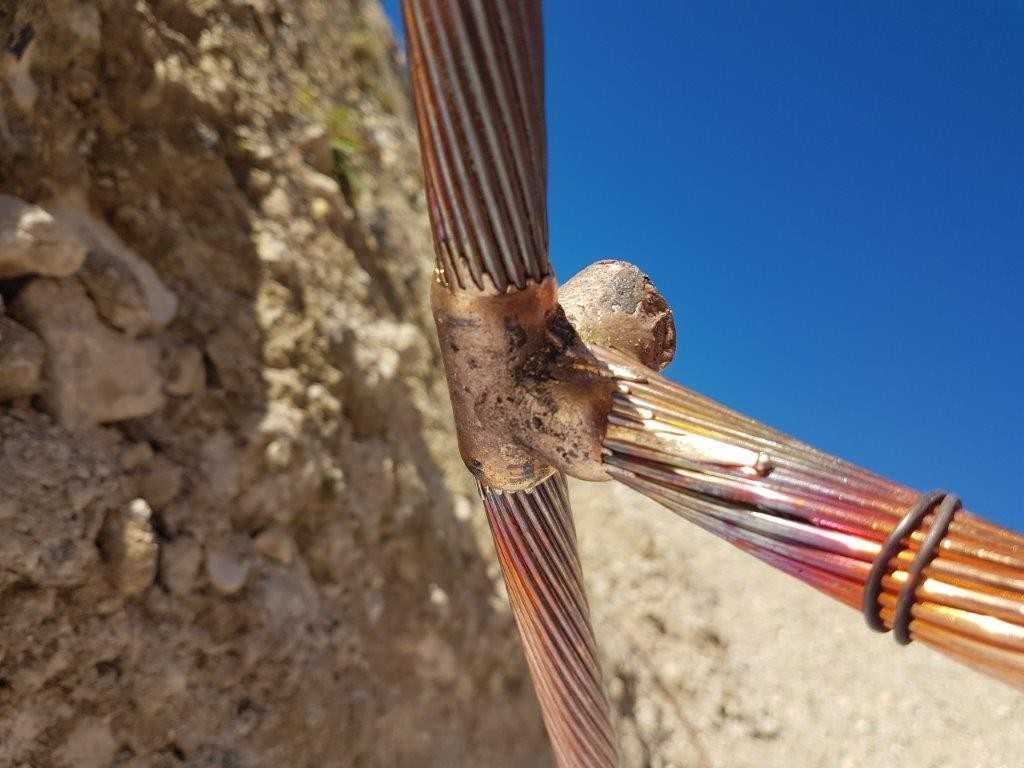
The steel dissolves (corrosion) bu depositing on copper (blackening) and in water. The difference of potential induced by the electric current is altering the less noble metal (the anode)
Material selection guide
Check the galvanic compatibility of materials
Choose compatible materials
Simply check the compatibility between the materials in contact. The columns and rows represent the two materials in contact:
- Green: The combination is safe
- Yellow: The combination presents a low risk
- Red: The combination is not suitable
| Couples galvaniques Galvanic series mV (millivolts) |
Acier inoxydable 304L Stainless steel 304L(1) |
Cuivre Copper(2) |
Bronzes Bronzes(2) |
Laiton Brass(2) |
Acier inoxydable type 316 Stainless steel A4 type(2) |
Etain Tin(3) |
Aciers Steels(3) |
Aluminium Aluminium(3) |
Acier galvanisé Galvanized steel(3) |
Zinc Zinc(3) |
| Acier inoxydable 304L Stainless steel 304L (1) |
0 | 320 | - | - | - | 550 | 750 | 840 | - | 1150 |
| Cuivre Copper (2) |
320 | 0 | 40 | 70 | 140 | 280 | 530 | 580 | 900 | 920 |
| Bronzes Bronzes (2) |
- | 40 | 0 | 30 | 100 | 240 | 490 | 540 | 860 | 880 |
| Laitons Brass (2) |
- | 70 | 30 | 0 | 70 | 210 | 460 | 510 | 830 | 850 |
| Acier inoxydable type 316 Stainless steel A4 type (2) |
- | 140 | 100 | 70 | 0 | 140 | 390 | 440 | 760 | 780 |
| Etain Tin (3) |
550 | 280 | 240 | 210 | 140 | 0 | 250 | 300 | 620 | 640 |
| Aciers Steels(3) |
750 | 530 | 490 | 460 | 390 | 250 | 0 | 50 | 370 | 390 |
| Aluminium Aluminum (3) |
840 | 580 | 540 | 510 | 440 | 300 | 50 | 0 | 320 | 340 |
| Acier galvanisé Galvanized steel (3) |
- | 900 | 860 | 830 | 760 | 620 | 370 | 320 | 0 | 20 |
| Zinc Zinc (3) |
1150 | 920 | 880 | 850 | 780 | 640 | 390 | 340 | 20 | 0 |
- (1) : High level of humidity
- (2) : Low level of humidity
- (3) : The metal is degraded
MALTEP Solutions
Discover MALTEP solutions
Simple and effective solutions
The range of MALTEP products includes a wide choice of materials, it is recommended to respect some simple rules in order to reduce the galvanic couple effect, to reduce the risk of corrosion and to ensure the sustainability of your equipments.
Respect as much as possible the homogeneity of the materials in contact
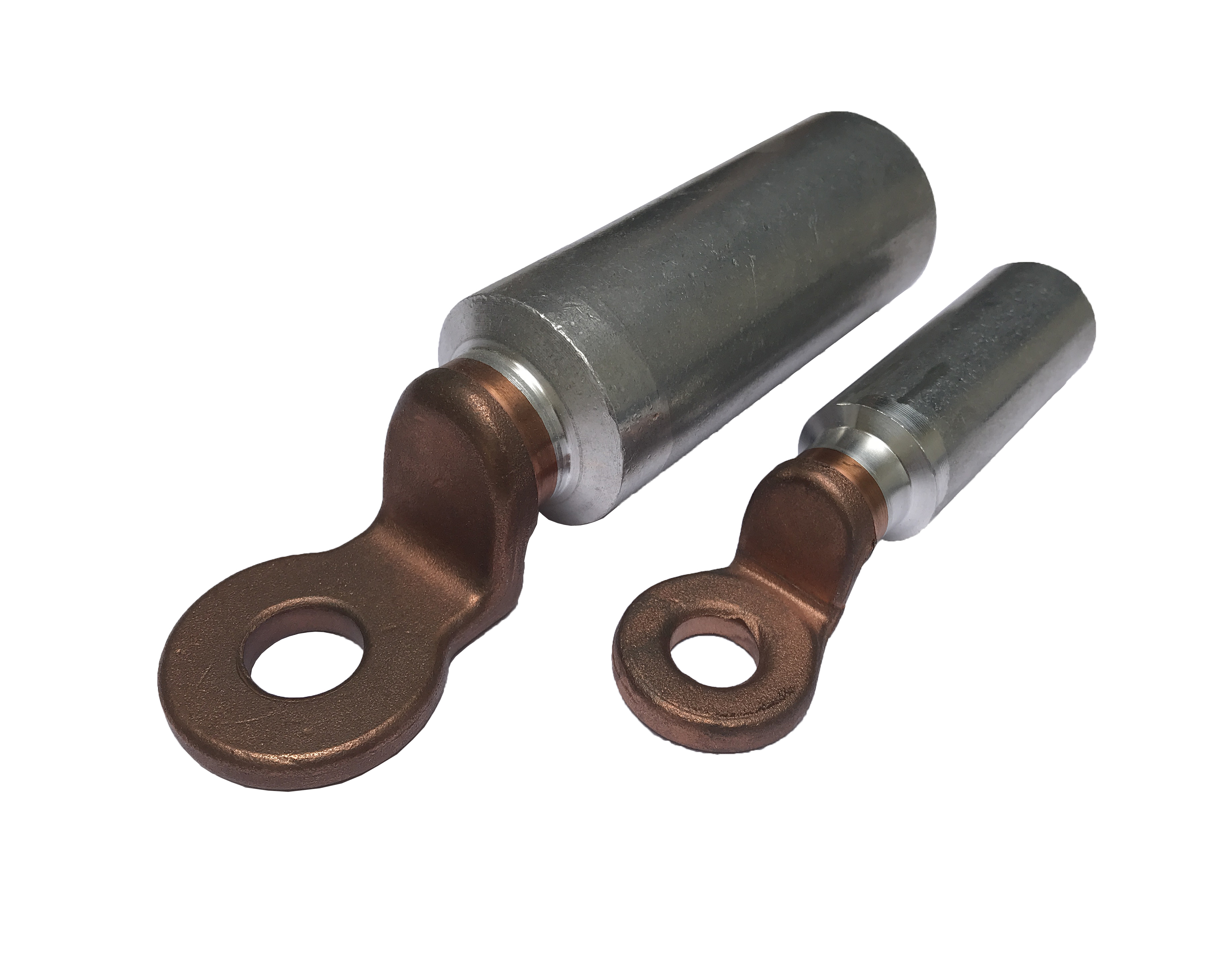
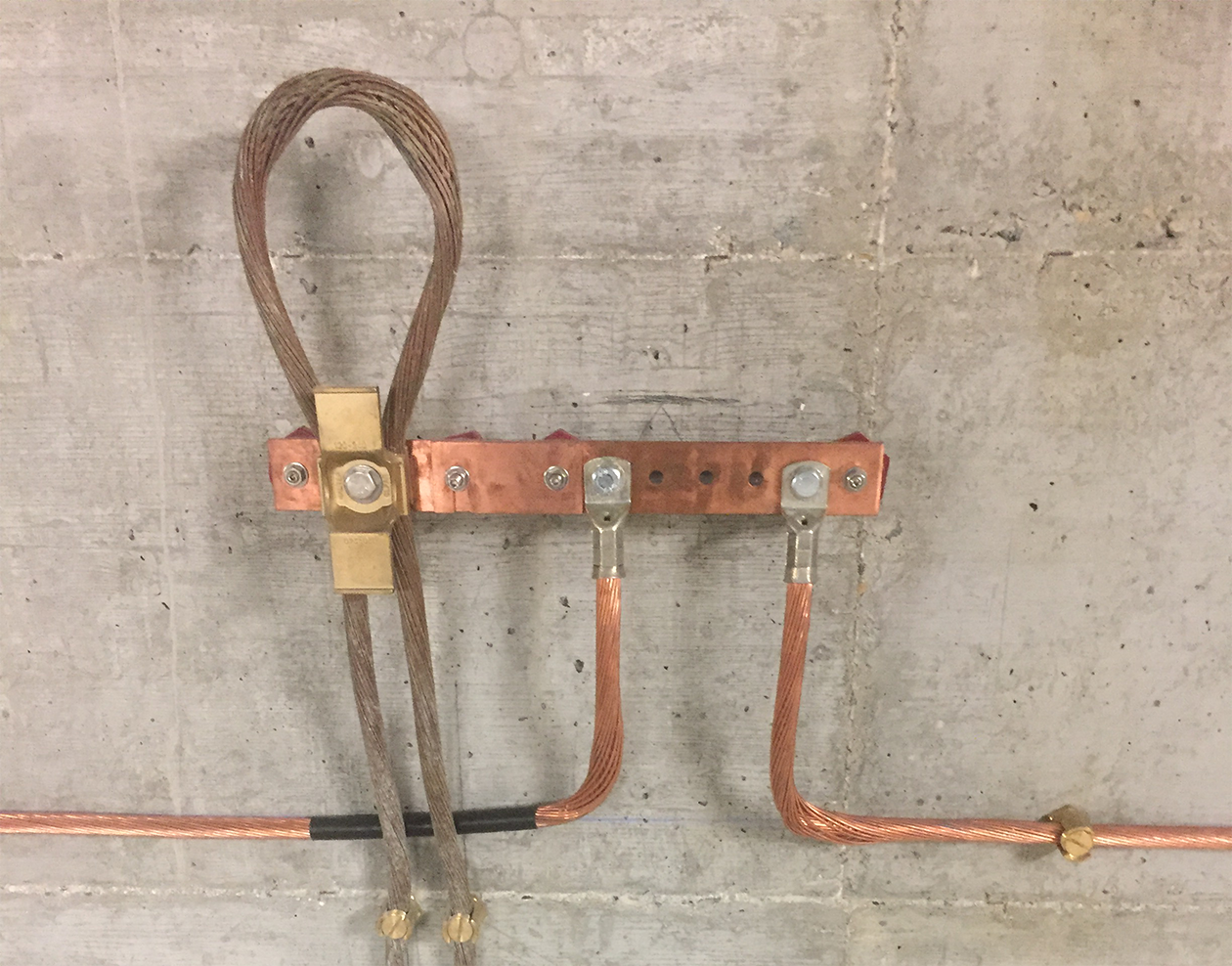
If the first solution is not possible, MALTEP offers different bimetallic products in copper and aluminium (lugs, plates and washers)
Discover some examples of products with bimetallic elements
Products range
Discover the MALTEP product range
MALTEP cable fastening solutions
MALTEP offers a complete range of solutions for the protection against the galvanic corrosion phenomenon
Cable holders
Bimetal compression lugs
Bimetal plates and washers








.JPG)
.JPG)
_1.JPG)
.JPG)
.jpg)
.jpg)